Omega-3 fatty acids found to control non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
11/15/2018 / By Tracey Watson

It is a little-known fact that even teetotalers can end up with liver disease. In fact, the most common form of this type of disease in the United States – non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) – affects close to 100 million people and can affect even those who drink little or no alcohol. While anyone of any age can end up with this potentially fatal illness, people in their 40s or 50s who carry excess weight around their bellies are most at risk. This condition often goes hand-in-hand with metabolic syndrome, the precursor to type 2 diabetes, which is also associated with increased abdominal fat, impaired ability to process insulin effectively, high blood pressure and elevated levels of a type of fat called triglycerides in the blood.
NAFLD is characterized by abnormally high levels of fat stored in the cells of the liver, and certain forms of the disease can cause liver inflammation and ultimately irreversible damage that can result in cirrhosis and even liver failure.
The good news is that a meta analysis of 18 studies, published in the journal Nutrition Reviews, found that supplementation with long-chain omega-3 fatty acids can help to manage NAFLD.
Omega-3s found to aid liver function
NUTRA Ingredients reported recently that on the basis of these most recent findings, all patients with NAFLD should be encouraged to supplement with specific dosages of omega-3 fatty acids.
In fact, the study authors advised that omega-3 supplementation, weight management and increased exercise “should be the first line of treatment for patients with NAFLD.”
So, exactly what is it in omega-3s that can help control NAFLD?
NUTRA Ingredients explained:
The mechanism of actions eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) adhere to in aiding liver function are not fully understood.
These omega-3 LC-PUFAs are thought to help promote genes involved [in] fatty acid oxidation whilst inhibiting genes involved in fatty acid production and storage.
Specifically, omega-3 LC-PUFAs may have a role in regulating both the rate of triglyceride production and its storage in the liver.
The researchers recommended that children with NAFLD be given a minimum of 250 milligrams of DHA each day, while adults should take no less than 3 grams of both EPA and DHA daily. Of course, weight reduction and regular exercise are also important components of a successful NAFLD control program.
Other amazing benefits of omega-3s
Managing NAFLD is not the only reason to supplement with omega-3, however. As previously reported by Natural News, omega-3s play a vital role in reducing inflammation and the diseases it causes, including cancer, stroke and heart disease. Hundreds of studies have also confirmed their ability to reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels, along with preventing autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis and allergies. (Related: The powerful role of omega-3 fatty acids in preventing diseases of inflammation — The experts speak.)
One study also found that omega-3 supplementation could reduce the risk of colorectal cancer in men not taking aspirin by an astounding 66 percent.
Foods high in omega-3
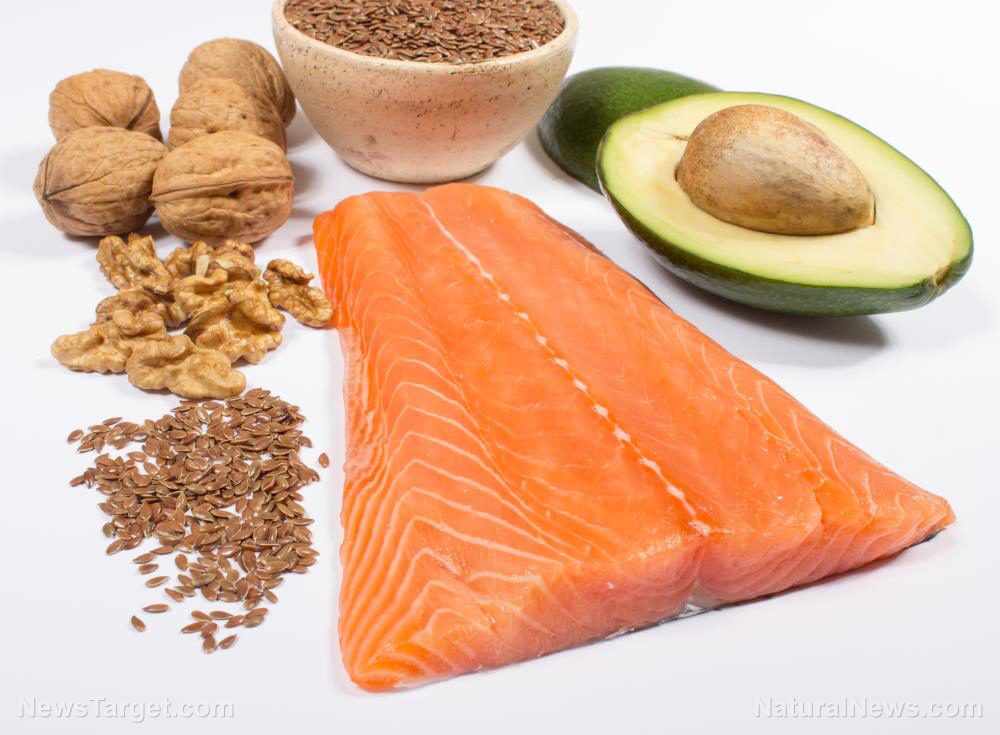
In addition to supplementing with a clean, trusted source of omega-3, it would also be good to increase consumption of foods high in this vital nutrient, including flax seeds, chia seeds, salmon (but make sure it doesn’t contain mercury), walnuts, shellfish like mussels and clams, navy beans, Brussels sprouts and avocados.
There are clearly excellent reasons to include omega-3 rich foods in your family’s diet. Not only are these foods delicious, but eating more of them will result in amazing long-term health benefits.
Learn more about the amazing health benefits of omega-3s at Nutrients.news.
Sources for this article include:
Tagged Under: liver health, metabolic syndrome, NAFLD, natural medicine, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, omega-3s