Can you prevent hepatitis B with this common dietary flavonoid?
09/28/2018 / By Edsel Cook
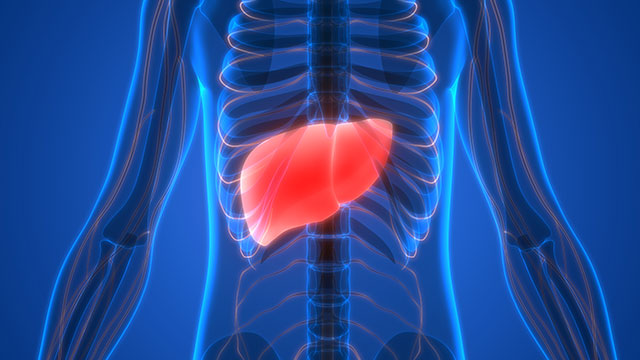
Commonly found in fruits, herbs, and vegetables, naringenin has been previously studied for its anti-inflammatory effects, as well as its ability to modulate the synthesis of hepatic apolipoproteins and lipids. A Taiwanese study reported that the dietary flavonoid is able to ameliorate hepatic steatosis induced by the hepatitis B virus protein X (HBx).
The study was made possible by a grant from the Buddhist Dalin Tzu Chi General Hospital. Its results were published in the scientific journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- The researchers constructed a mice model using HBx-transgenic animals. They administered naringenin via oral gavage to some of the mice every day for 14 days. Untreated animals served as the control for the study.
- At the end of the period, all mice were sacrificed. Researchers collected liver tissues and sera for histopathology and biochemical analysis.
- According to the analysis, naringenin prevented the accumulation of hepatic lipids in the livers of HBx-transgenic mice. The flavonoid also counteracted liver dysfunction caused by the hepatitis B virus.
- Furthermore, naringenin greatly reduced the expression of adipogenic and lipogenic genes in the mice. These genes are involved in HBx-mediated hepatic steatosis, as they create adipose tissue and fatty acids that comprise lipids.
- The analysis suggests that naringenin suppressed the transcription process of HBx-induced genes like SREBP1c, LXR?, and PPAR? in HBx-transgenic mice. It similarly suppressed human HepG2 liver cells that were transfected by HBx from mice liver samples.
The results of the mice model experiment point to the potential use of naringenin in preventing the onset of HBx-induced hepatic steatosis in humans. This is significant because hepatic steatosis is a risk factor for other liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhosis, and of course hepatitis B.
Find the full text of the study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Lin H-J, Ku K-L, Lin I-H, Yeh C-C. NARINGENIN ATTENUATES HEPATITIS B VIRUS X PROTEIN-INDUCED HEPATIC STEATOSIS. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017;17(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-2019-2.
Tagged Under: fatty liver disease, flavonoids, hepatic steatosis, hepatitis B, hepatitis B virus, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cirrhosis, liver health, naringenin, nutrients, nutrition, phytochemicals, science