The ethnomedicinal use of shea butter in treating salmonella infections
08/02/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
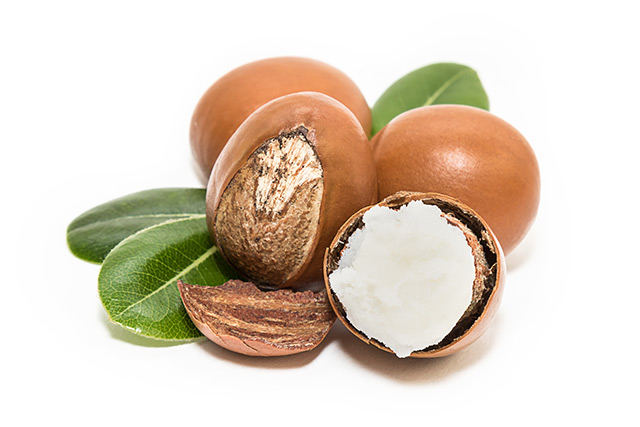

Researchers at the University of Dschang, University of Ngaoundéré, and University of Yaoundé 1 in Cameroon assessed the effects of shea butter (Vitellaria paradoxa) on treating Salmonella infection. The study, published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, provided scientific evidence on the ability of shea butter in treating salmonellosis.
- The researchers administered shea butter leaf extracts on mice infected with Salmonella typhimurium for up to 18 days.
- Then, they looked at the serum markers, including total protein, creatinine, transaminases, bilirubin, and lipid profile of mice to examine the effects of the shea butter extract treatment.
- In addition, they tested the safety and looked at the phytochemicals of the shea butter leaf extract by conducting acute toxicity test and phytochemical screening.
- Results revealed that the aqueous extract of shea butter leaf eliminated salmonellosis in previously infected mice within twelve days of treatment.
- Although the Salmonella infection significantly increased transaminases activity and significantly decreased the relative weight of liver and kidney and protein content of the mice, these damages were improved through the administration of the plant extract at higher doses.
- The treatment did not cause any toxic effect, but it may have a sedative effect on the central nervous system, may promote a decrease in plasma levels of algogenic substances, and may cause diarrhea at high doses.
- Based on the results of the phytochemical screening, alkaloids, anthocyanins, anthraquinones, flavonoids, phenols and polyphenols, saponins, steroids, band tannins were present in shea butter leaf extracts.
In conclusion, shea butter tree contains antimicrobial substances that can help treat Salmonella infection and typhoid fever.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
To read more stories on natural medicines like shea butter, visit AlternativeMedicine.news today.
Journal Reference:
Fodouop SP, Tala SD, Keilah LP, Kodjio N, Yemele MD, Nwabo AHK, Nji-kah B, Tchoumboue J, Gatsing D. EFFECTS OF VITELLARIA PARADOXA (C.F. GAERTN.) AQUEOUS LEAF EXTRACT ADMINISTRATION ON SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM-INFECTED RATS. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 21 March 2017; 17(160). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1643-1
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, natural cures, natural medicine, Salmonella, salmonella infection, salmonellosis, shea butter, shea butter leaf extracts, typhoid fever, Vitellaria paradoxa